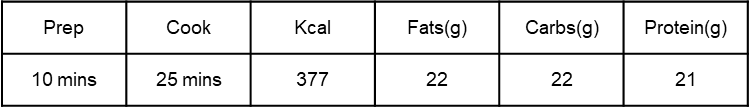
You are protein, so don’t think you don’t need to worry about it! Here’s why it’s so important and how to ensure you’re getting enough.
Protein is one of the most important nutrients for our bodies, but many of us don’t realize just how vital it is.
Contrary to popular belief, we do not only need protein when we are trying to bulk up or lose weight – it is an essential part of our diet no matter what.
In this blog post, I will discuss the benefits of protein, why we should all be making sure we are meeting our recommended intake, and some tips on how to do so.
So read on, and let’s learn together!
What Is Protein?
Chances are, if you’re reading this, you’re at least somewhat interested in fitness and working out.
And if you’re interested in working out, you’ve probably heard the word “protein” thrown around a lot.
But what is protein, really?
Protein is a macronutrient that is essential to the human body.
It is made up of amino acids, which are the building blocks of muscle tissue.
When you eat foods that contain protein, your body breaks down the protein into its building blocks (amino acids) and uses them for various functions.
With that in mind, let’s talk a bit about the functions of protein.
Functions Of Protein
As you probably know by now, protein is an essential macronutrient that plays a major role in human health.
Essential means that the body needs it for optimal functioning but can’t produce it on its own.
It is involved in nearly every cellular process and is essential for the structure and function of all tissues.
In addition, protein provides the body with glucose at times when carbohydrates are not available and also helps to regulate metabolism.
Let’s have a look at the 3 most important functions of protein!
Recovery
Why do we need protein? To put it simply, our cells need it to function properly. We have trillions of cells in our bodies, and they’re constantly breaking down and rebuilding.
Protein is the key component that helps our cells rebuild, and without it, we would basically fall apart.
Protein is also essential for recovery after exercise. When we work out, we create tiny tears in our muscle fibers.
In order for our muscles to repair and grow stronger, they need protein. That’s why athletes often include protein-rich foods in their post-workout recovery meals.
This is the first and perhaps most important function of protein.
Hormone Production
If you’re like most people, you probably think of protein as something you eat to build muscle.
And while it’s true that protein is essential for muscle growth, it’s also important for a wide range of other bodily functions.
For example, protein is necessary for the production of hormones, which help to regulate metabolism and basically most processes in the body.
So, next time you’re chowing down on a steak or slurping up some good ol’ raw milk, remember that you’re not just satisfying your appetite or giving your muscles nutrients —you’re also helping to keep your body running like a well-oiled machine.
All-around.
Enzymes
Enzymes are biochemical machines responsible for regulating chemical reactions in the human body, and they are found in all living cells.
They are essential for digestion, muscle, nerve function, and thousands of other roles.
Enzymes are essential for life because they help to build some substances and break down others, all of which help our bodies THRIVE!
Without enzymes, proteins would not be able to perform their essential functions.
And vice versa, without sufficient protein of good quality, your enzymes won’t do their best!
But what are good quality sources of protein? Let’s have a look!
Best Protein Sources
Most people know that they need to eat protein-rich foods in order to build muscle, but few know which foods are the best sources of this important nutrient.
If that sounds familiar, let’s take a closer look at some of the best sources of protein!
Animal Products
While there are many sources of protein out there, animal products like meat, organs, eggs and dairy are generally considered to be the best.
This is because they contain all of the essential amino acids that our bodies need, and they’re also very bioavailable, meaning that our bodies can easily absorb and use them.
So if you’re looking to up your protein intake, animal products are definitely the way to go.
Think of:
- Beef meat (both lean and fatty cuts)
- Organs
- Chicken
- Lamb
- Pork
- Eggs
- Feta cheese
- Yellow cheese
- Other dairy products
Fish & Other Seafood
As we said, animal meat is a great source of protein, but if you don’t quite like animal meat, you can also resort to fish and other seafoods, as those are also abundant of high-quality protein.
Besides that, seafood also has other great nutrients, like omega-3s, other healthy fats and let’s not forget – It’s tasty!
Add the following foods to your menu:
1. Salmon & other fish
2. Shrimp
3. Crabs
4. Lobsters
5. Caviar
6. Calamari
7. Mussells
Plant Sources
Did you know that there are 20 different amino acids that are needed to form a protein? Out of these 20, 9 are essential, meaning our bodies can’t produce them, we must get them from food sources.
Animal proteins contain all 9 of these essential amino acids, which is why they’re considered ‘complete’ proteins.
However, most plant sources of protein lack one or more of these essential amino acids.
This doesn’t mean that you can’t get protein from plants, though.
It just means you have to be a bit more creative in your food combinations. For example, you could pair rice with beans or nuts with seeds to make a complete protein.
Here are our favorite plant sources of protein:
- Beans
- Peanuts
- Lentils
- Tofu
- Tempeh
Final Words
So, what does this mean for you as an athlete or fitness enthusiast? It means that you need to prioritize protein in your diet. Remember – you are protein!
Protein is essential for repairing and building muscle tissue post-workout, and it’s also important for the maintenance of your body, overall.
This is why it’s important that you make sure you’re getting enough of it (about 0.8-1g of protein per pound of bodyweight.)
What are your favorite sources of protein?
You are protein – so:
Want to learn more about protein?
Download our free eGuide “Fundamentals of Nutrition: Protein”
You might like this blog: Nutrition For Fitness-What Truly Matters